Question:
Why does damping affect the resonance amplitude?
Answer:
A forced oscillation attains its final amplitude when the rate of input of energy (from the driver) matches the rate of loss of energy (to the surrounding).
–
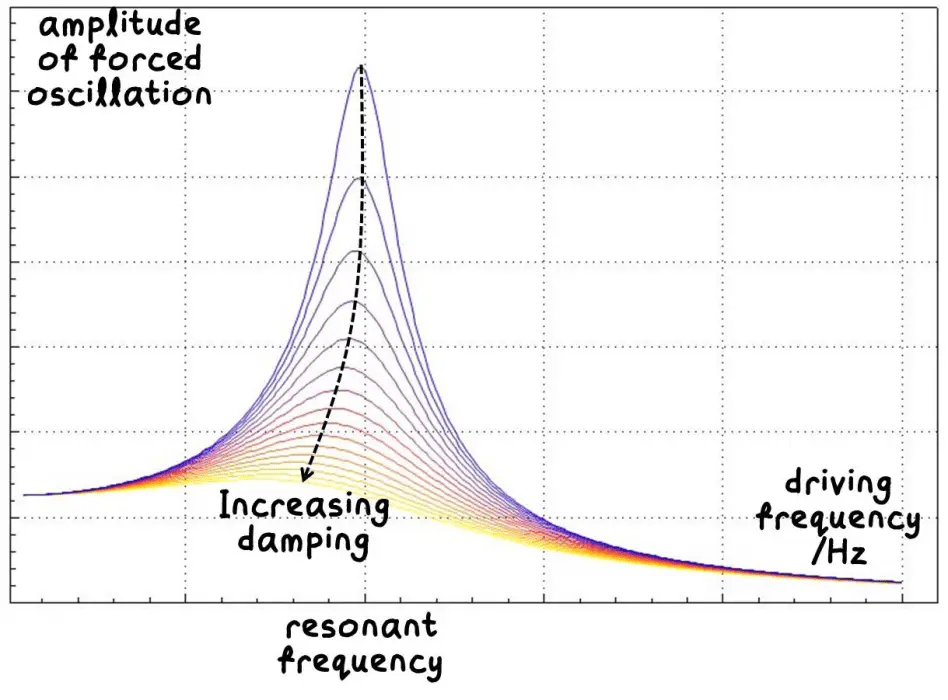
The rate of loss of energy is dependent on (1) the amplitude of oscillation and (2) the degree of damping. As the amplitude of the forced oscillation grows, the rate of energy loss due to damping also increases.
So if the degree of damping is high, the forced oscillation will reach the equilibrium state at a smaller amplitude. (Kind of similar to why larger air resistance results in lower terminal velocity for falling objects) This explains why the stronger the damping, the lower the resonance peak.
–
^ In theory, if there is no damping, the amplitude of forced oscillation should grow indefinitely. In practice, however, the oscillation would have broken down at some stage to end the party.