How do the passengers not drop out of the car when they are inverted at the top of the loop?
The following video explains why.
Category: 06 Circular Motion
How do the passengers not drop out of the car when they are inverted at the top of the loop?
The following video explains why.
As the ball loses speed, it eventually becomes too slow to complete the loop successfully. Why?
–
All the circular motion featured here have very similar dynamics.
(1) Conical Pendulum
–
(2) Flying Chairs
–
(3) Airplane turning a horizontal circle
–
(4) Cars turning on banked curve
NASCAR race cars do not slow down when they turn. The tracks are banked (slanted) at the bends. Banking allows the cars to utilize the normal contact force that the track surface exerts on the cars to help provide the required centripetal force. This allows NASCAR to turn at full speed. In fact, at particular speed and angles, the cars can negotiate the bends without the tires providing any sideway frictional force at all. The following video explains.
When we see the bodies pinned against the wall, it is tempting to imagine that there are some centrifugal forces pushing those people outward against the wall. But there is none. The motion is fully explained by the presence of a centripetal force, not a centrifugal force.
–
The same principle is being applied by these stuntmen. The key to pulling off this stunt successfully is to ride at a high speed. The inertia of the bike (tendency to keep moving straight) causes it to pressed hard against the wall, resulting in a large normal contact force. A large normal contact force is crucial because the amount of friction depends on it. It is the frictional force that holds up the weight of the car.
–
Quantitatively, the magnitude of the required centripetal force is related to the speed and radius of circular motion by the formula F=mv2/r.

–
For the same v, a stronger centripetal force F would result in a tighter circular motion (smaller r). In the animation below, the objects are experiencing centripetal forces of 4F, 2F and F, resulting in circular motion of radii R, 2R and 4R.
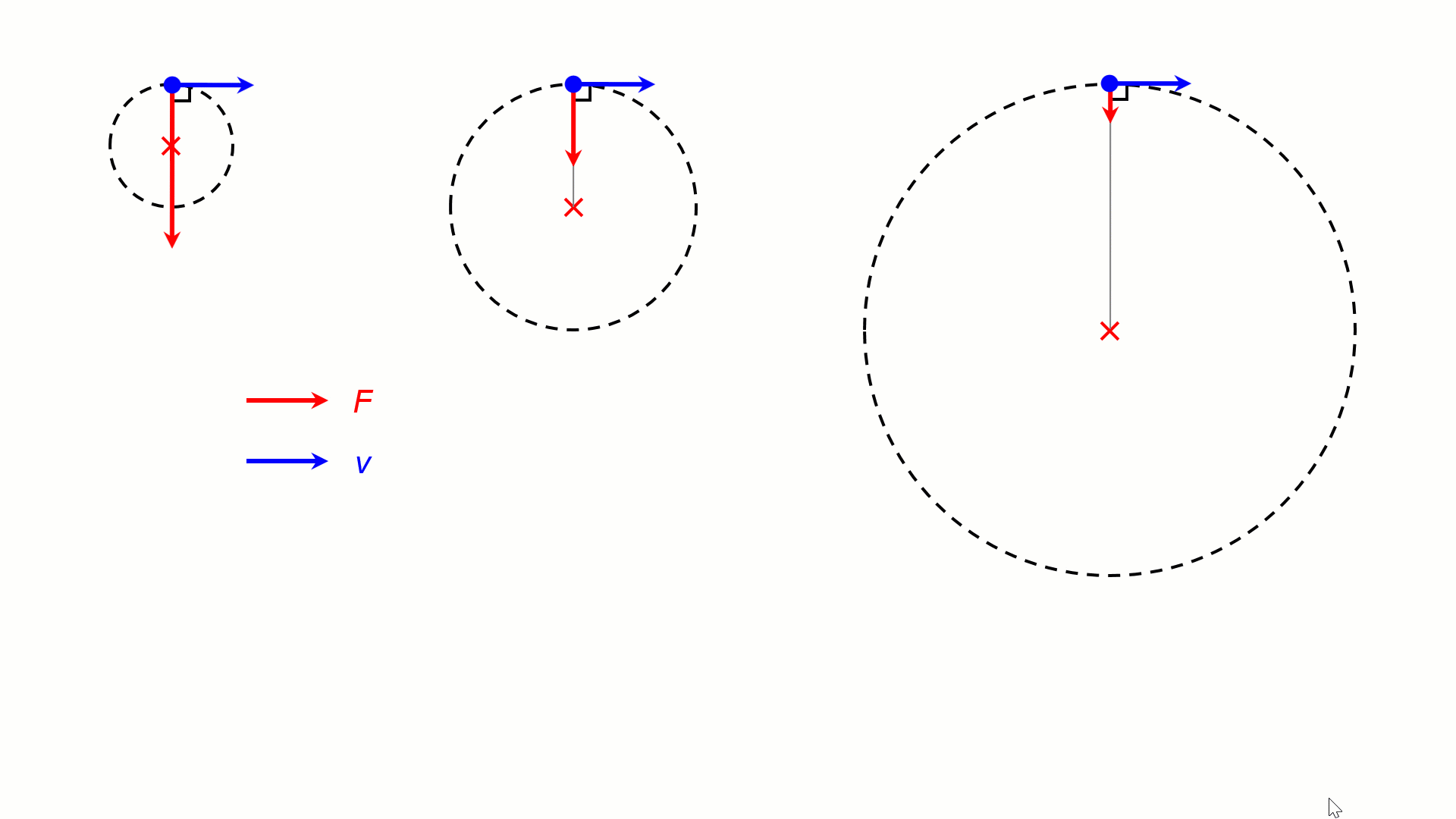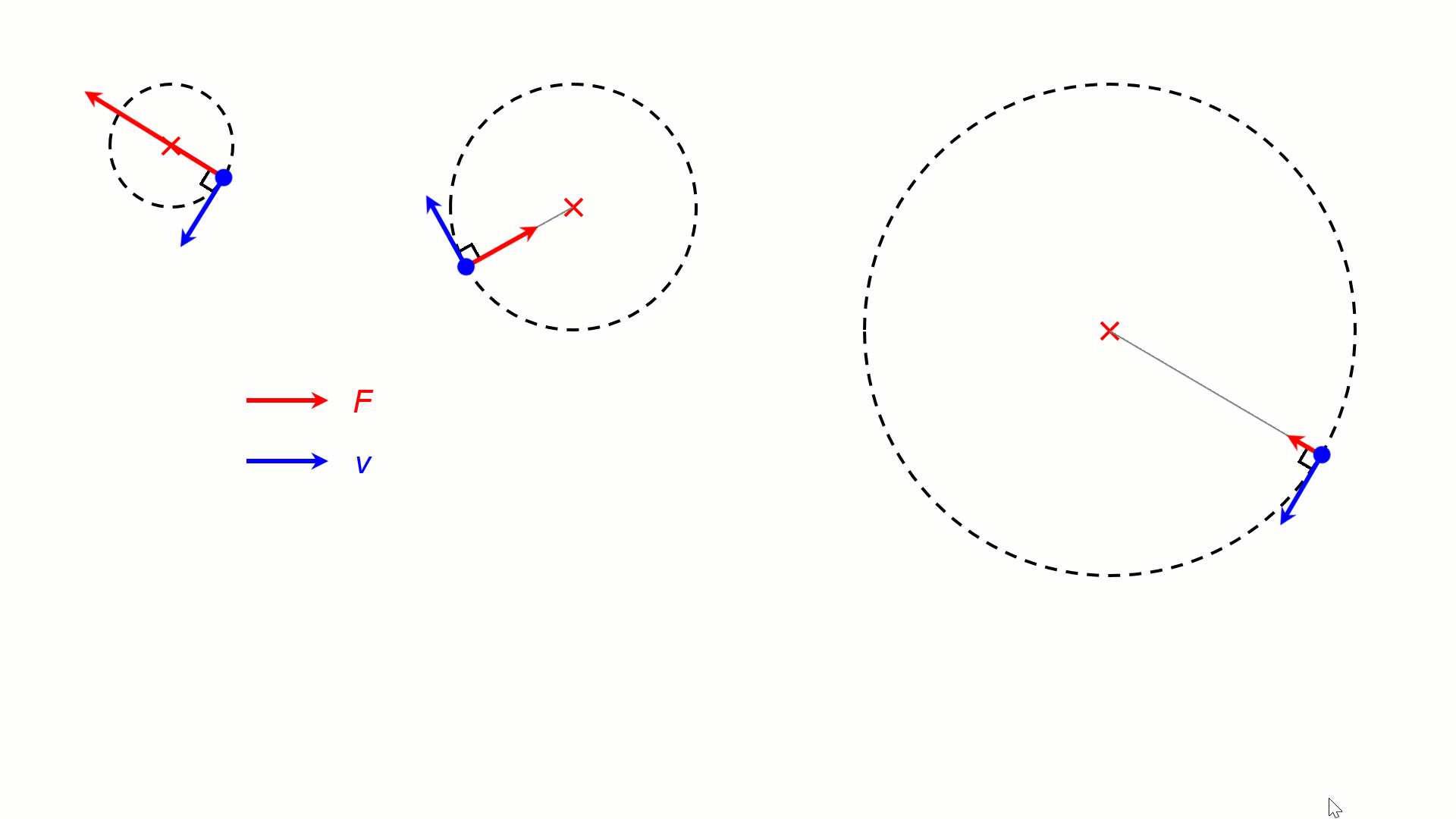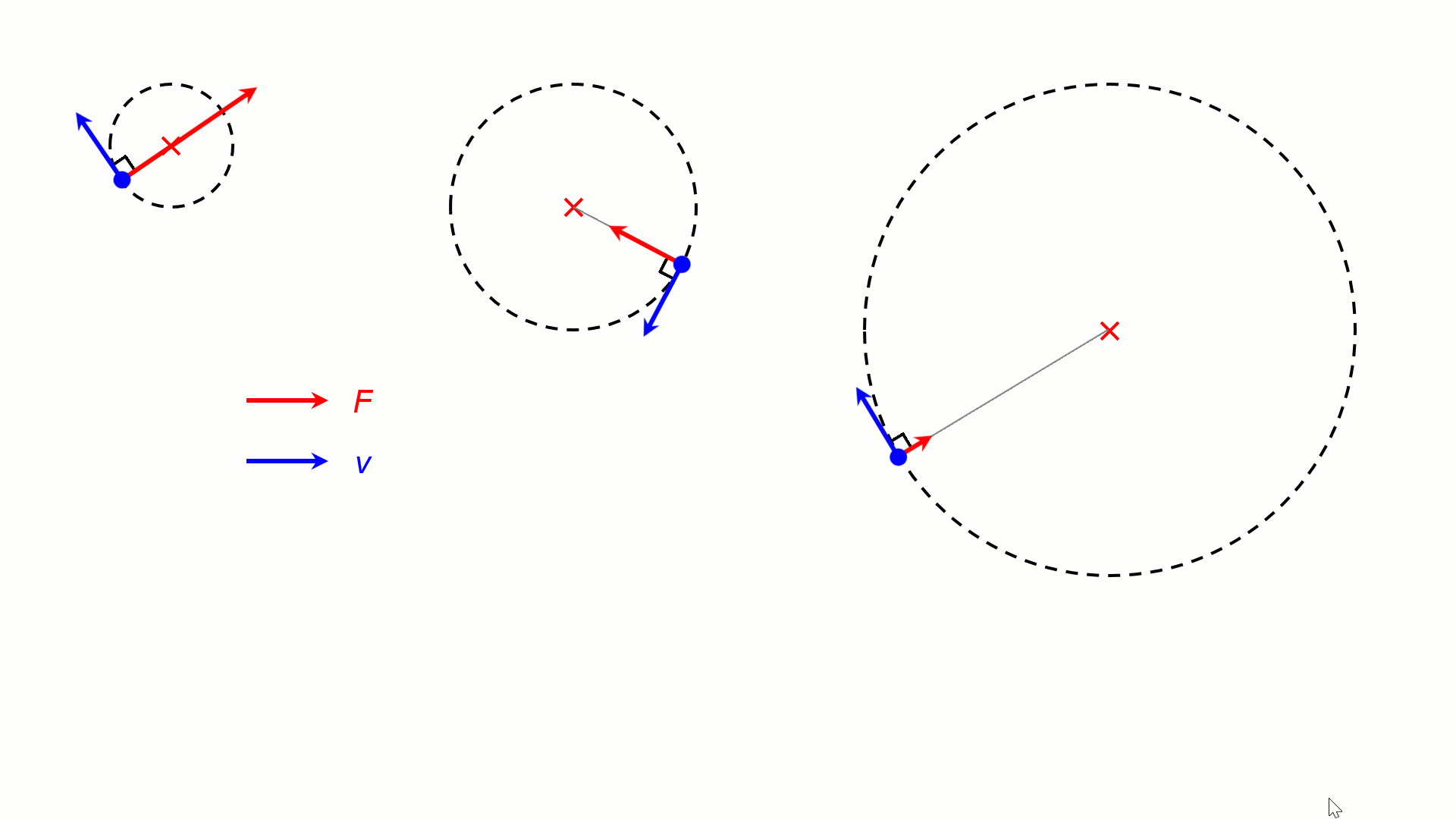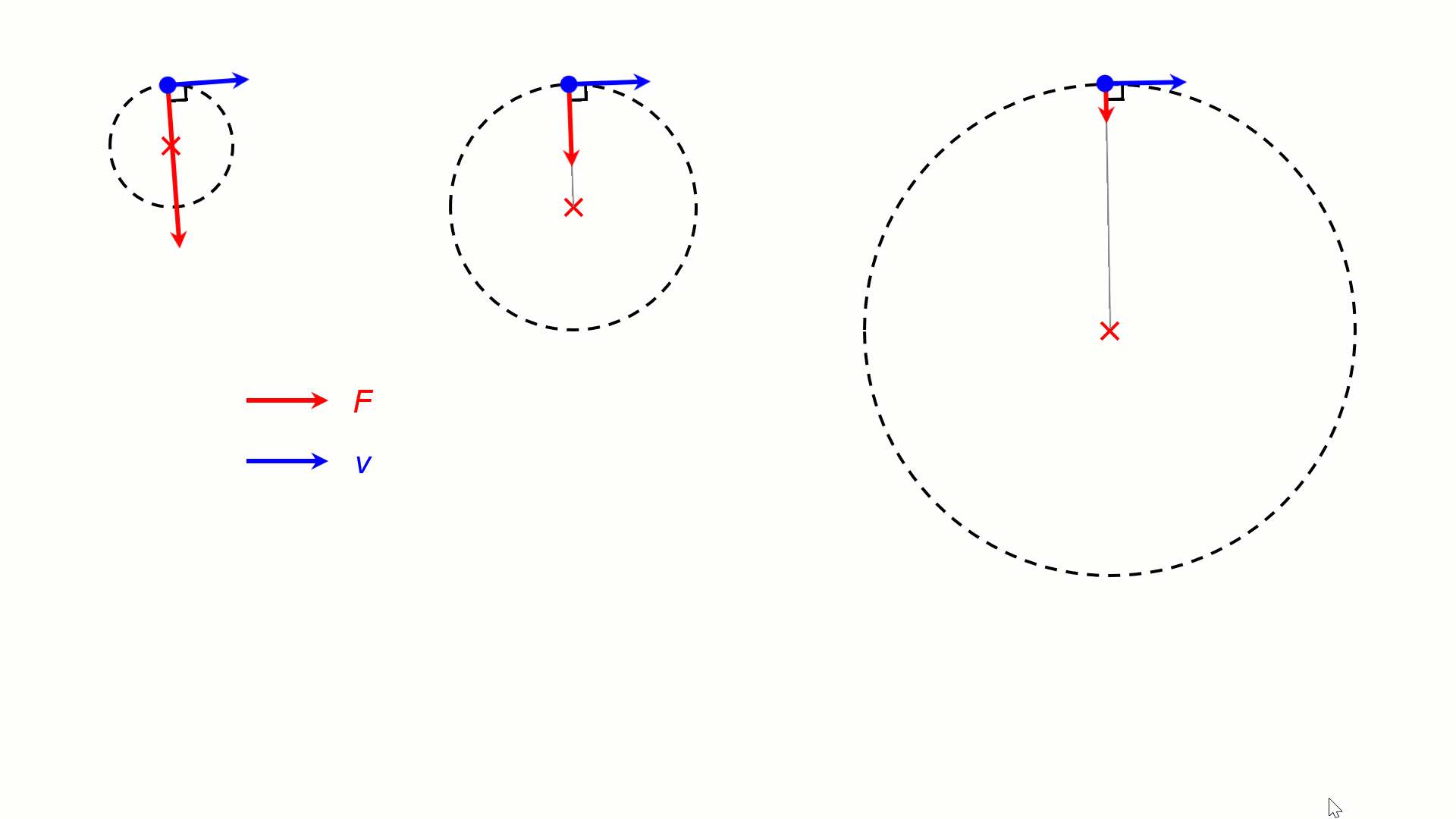
–
For the same centripetal force F, a lower speed v would result in a tighter circular motion (smaller r). In the animation below, the objects have speeds of 1/√2 v, v and √2v, resulting in circular motion of radii R, 2R and 4R.
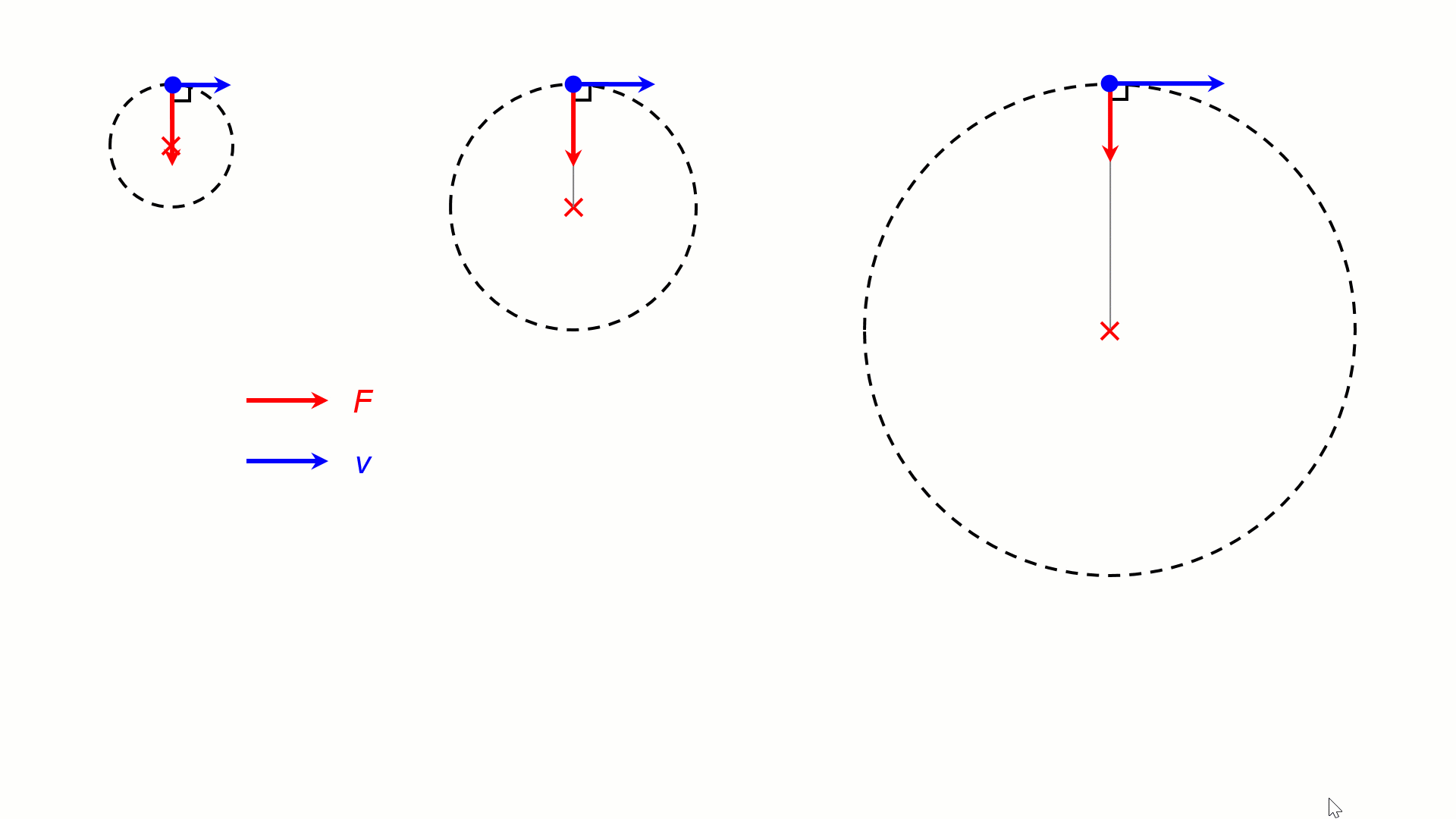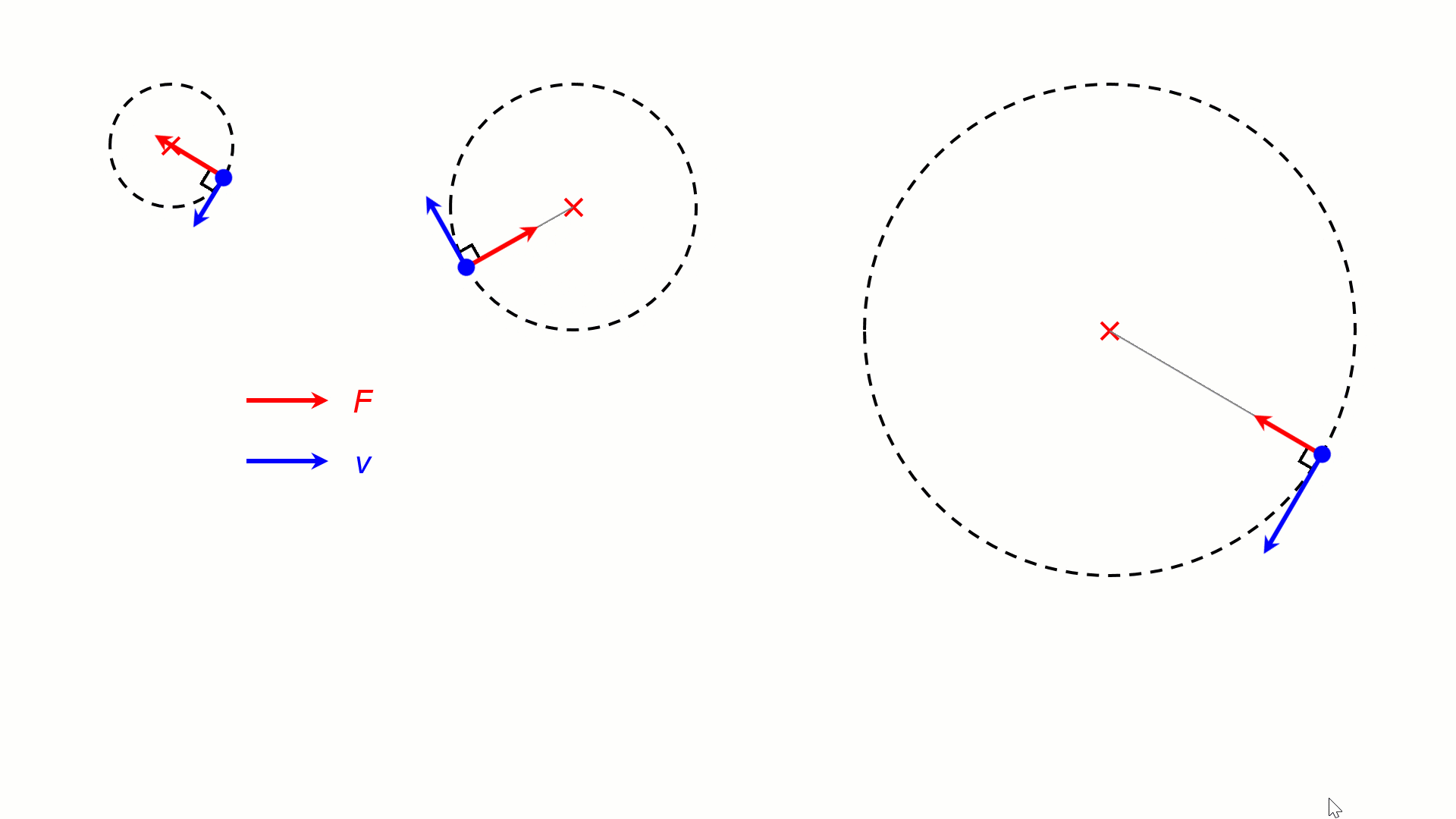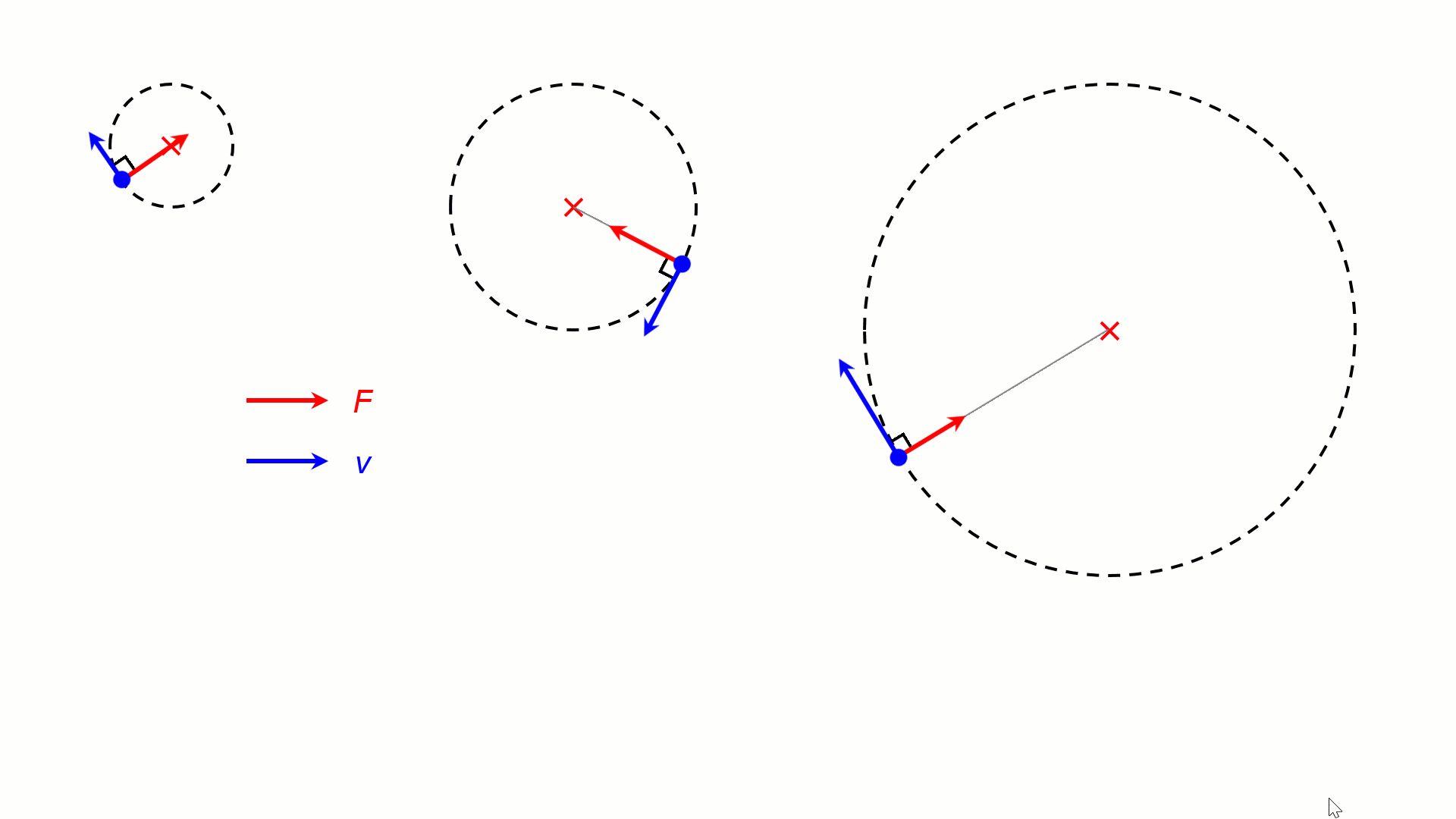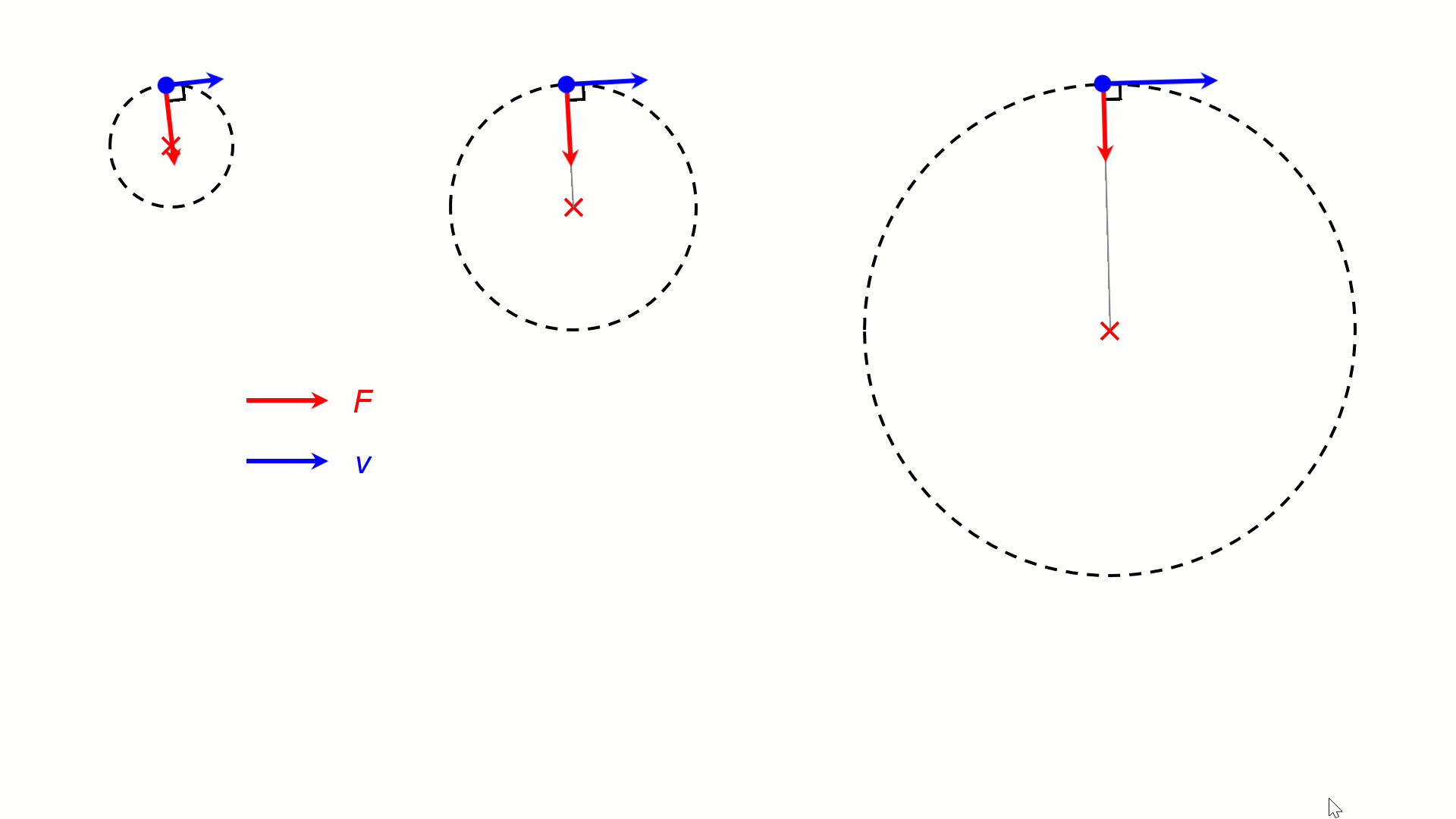
 The direction of the velocity continuously change towards the centre of the circle, but the magnitude of the velocity is constant. Uniform circular motion is accelerated motion. The acceleration is in the centripetal direction.
The direction of the velocity continuously change towards the centre of the circle, but the magnitude of the velocity is constant. Uniform circular motion is accelerated motion. The acceleration is in the centripetal direction.
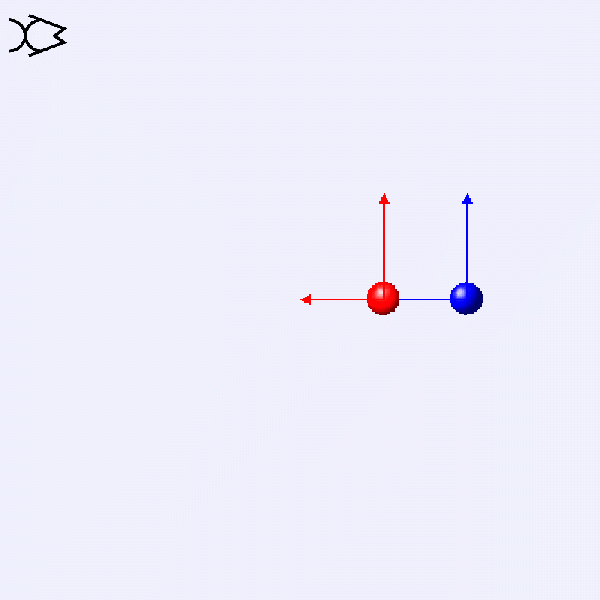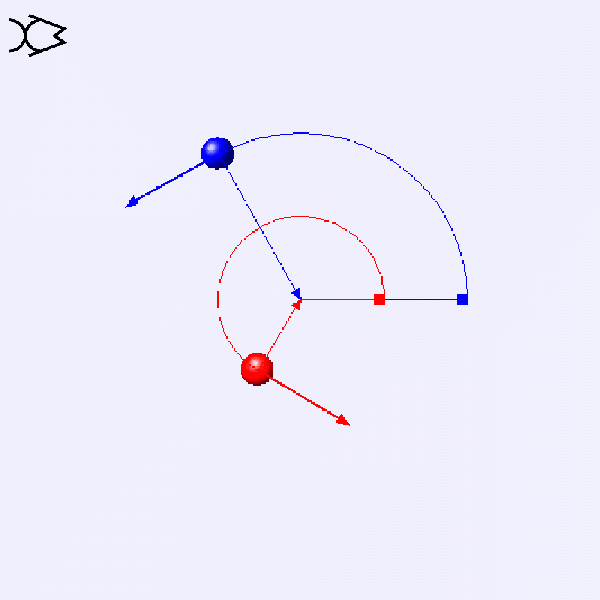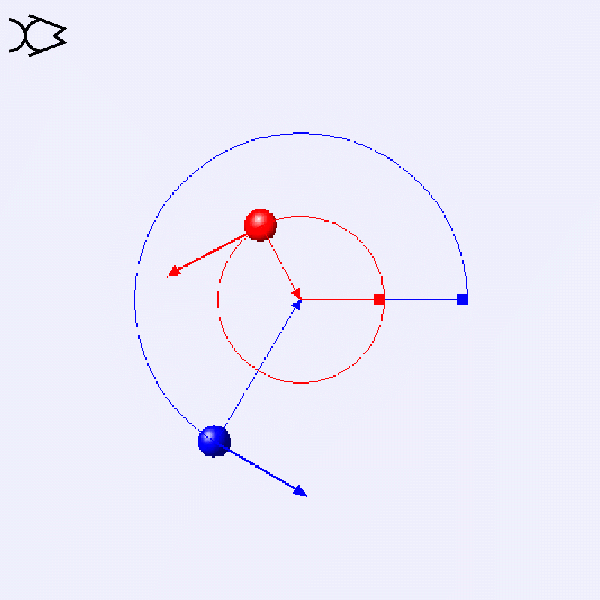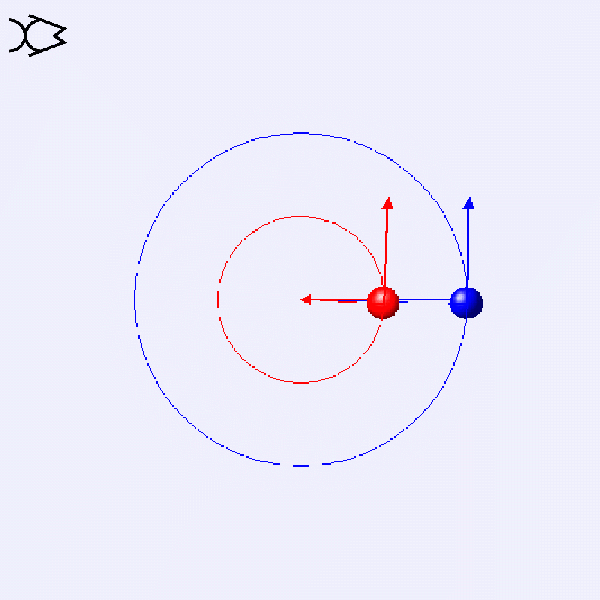
How do the linear velocity v and angular velocity ω of these two circular motions compare?
–
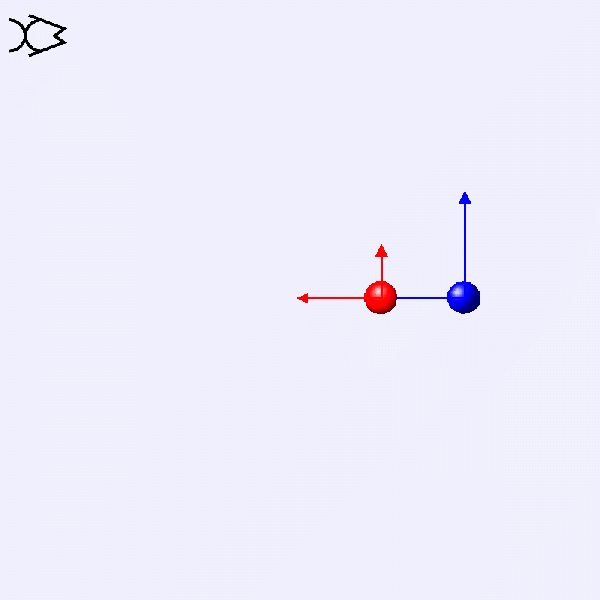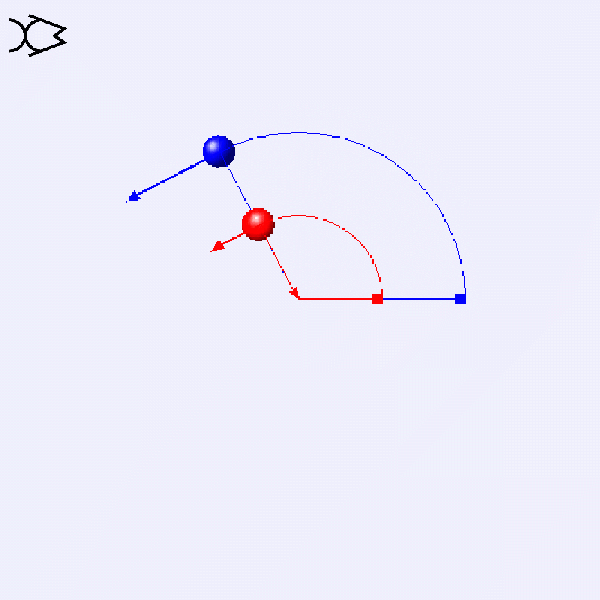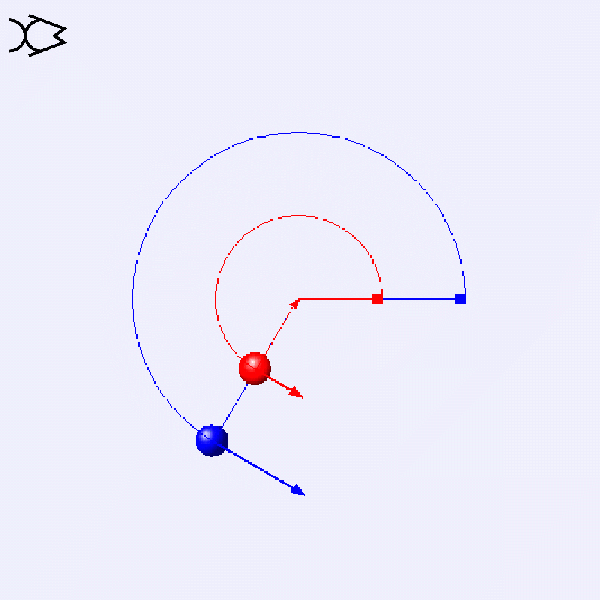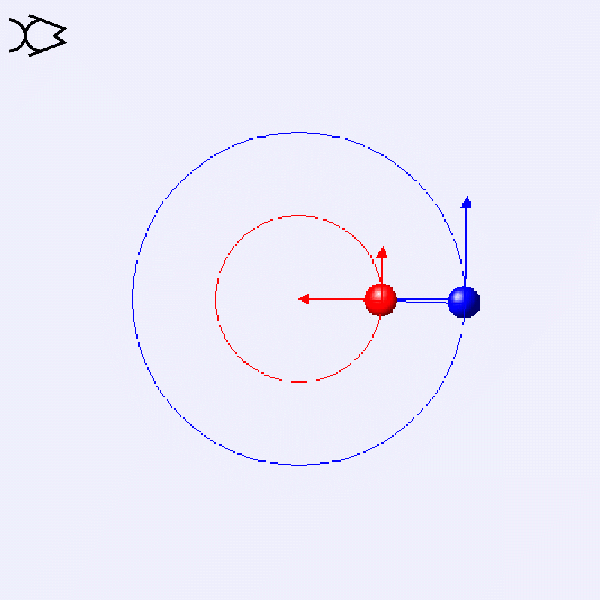
v=rω
These two circular motions have the same ω. The blue one has twice the radius, so its v is double that of the red one.
–
ω=v/r
These two circular motions have the same v. The blue one has twice the radius, so its ω is half that of the red one.